Secondary mastoid obliteration improves quality of life for patients with chronic otitis media
Image: PD
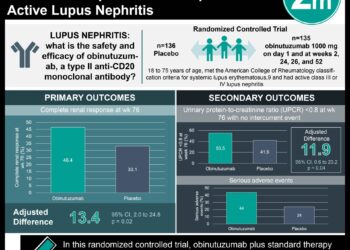
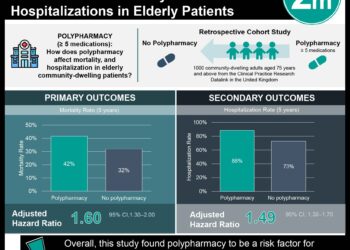
1. When compared to primary mastoid obliteration, secondary obliteration resulted in a more pronounced, though not statistically significant, improvement in quality of life.
2. In both the secondary and primary obliteration groups, a significant improvement in quality of life was noted.
Evidence Rating Level: 2 (Good)
Study Rundown: During mastoidectomy, cavity obliteration and reconstruction of the bony external ear canal is often recommended. If the obliteration is not completed during the procedure (primary obliteration), the cavity may not heal and a secondary obliteration procedure may be necessary. The authors used the Glasgow Benefit Inventory to assess quality of life (QOL) changes in patients following primary and secondary mastoid cavity obliteration. A subsequent analysis demonstrated a more pronounced, though not statistically significant, QOL improvement in the secondary obliteration group. The much smaller number of patients in the secondary obliteration group may explain the lack of significance.
Click to read the study in Journal of Otolaryngology – Head & Neck Surgery
Relevant Reading: Quality-of-life assessment after primary and revision ear surgery using the chronic ear survey
In-Depth [retrospective cohort]: This study compared the QOL improvement in 46 patients who had primary mastoid cavity obliteration and 12 who needed secondary obliteration. The 58 patients completed the Glasgow Benefit Inventory, either in person or over the phone. In the secondary obliteration group 83% of the subjects reported improvement in QOL compared to only 72% in the primary obliteration group. The secondary group also reported greater improvement of QOL across the GBI subscales (general, physical, and social). While these differences were noted clinically, they were not statistically significant on a Mann Whitney U test (p = .10, p = .15, and p = .43 respectively).
By Amir Tarsha and Chaz Carrier
More from this author: Local excision inferior to major resection in T1-2 colon cancer and T2 rectal cancer
© 2013 2minutemedicine.com. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2minutemedicine.com. Disclaimer: We present factual information directly from peer reviewed medical journals. No post should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors, editors, staff or by 2minutemedicine.com. PLEASE SEE A HEALTHCARE PROVIDER IN YOUR AREA IF YOU SEEK MEDICAL ADVICE OF ANY SORT.