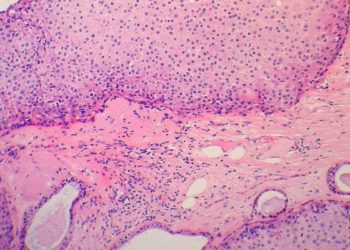
Captopril mitigates radiation-induced lung fibrosis in rats
Image: PD
1. Captopril or the synthetic antioxidant, EUK-207, reduced functional, biochemical, and histopathological signs of lung fibrosis after whole thoracic radiation.
2. The combination of captopril and EUK-207 was incrementally superior at reducing fibrosis than either agent alone.
Evidence rating: 2 (Good)
Study Rundown: Radiation therapy is a mainstay in the treatment of lung cancer. Despite advances in technologies that have allowed radiation to be more precisely directed at tumors, normal lung tissue is also unavoidably irradiated. The result is inflammation and fibrosis that may lead to pneumonitis, which can be lethal. It has been shown that both antioxidants and angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors mitigate collateral toxicity to normal lung. In this study, the authors show that the synthetic antioxidant EUK-207 and captopril are effective in reducing functional, biochemical, and histopathological indicators of inflammation and fibrosis in rats that were irradiated. This study was limited by its short endpoint of 32 weeks. The authors also selected a species of rats that are especially prone to radiation-induced fibrosis, which may have biased the results to improvement with any agent. There was also no pharmacological control group.
Click to read the study in International Journal of Radiation Oncology
Relevant reading: Radiation damage to the lung: Mitigation by angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors
In Depth [Basic Science Study]: In this study, female SD rats were separated into six groups, consisting of eight rats each: untreated control, WTR alone, WTR and EUK-207, WTR and captopril, WTR and captopril plus EUK-207, or EUK-207 plus captopril without radiation. 11 Gy of radiation was delivered using an image-guided animal irradiator. From one week to 14 weeks post-irradiation, rats were treated according to their group design and then sacrificed at 32 weeks. Inflammation was estimated with 8-hydroxy-2-deoxyguanosine staining (8-OHdG), malonidaldehyde levels (MDA), and macrophage activation (ED-1). TGF-beta staining and hydroxyproline levels were used as proxy measures of fibrosis. At 32 weeks, the breathing rate for the WTR group and WTR + captopril plus EUK-207 group was 200 and 150, respectively (P<0.01). The relative expression of 8-OHdG for WTR group and WTR + captopril plus EUK-207 group were 15 and 7.3, respectively (P<0.01); MDA levels were 11 and 3, respectively (P<0.01); ED-1 were 7.5 and 4, respectively. Similarly, hydroxyproline levels for WTR group and WTR + captopril plus EUK-207 group were 160ug and 70ug, respectively (P<0.01), while TGF-beta relative expression was 43 and 10, respectively (P<0.01). For 8-OHdG and ED-1, the combined treatment group was superior to single therapy alone. Statistical analysis was performed using ANOVA and Tukey method of least-square means.
More from this author: Erlotinib does not demonstrate increased survival in ovarian epithelial carcinomas, Afatinib shows increased progression-free survival in non-small-cell lung cancer, Radiosurgery alone may be effective for some arteriovenous malformations, Escalated-dose radiotherapy did not increase survival in prostate cancer, Stereotactic radiosurgery promising for patients with multiple brain metastases
©2012-2014 2minutemedicine.com. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2minutemedicine.com. Disclaimer: We present factual information directly from peer reviewed medical journals. No post should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors, editors, staff or by 2minutemedicine.com. PLEASE SEE A HEALTHCARE PROVIDER IN YOUR AREA IF YOU SEEK MEDICAL ADVICE OF ANY SORT.