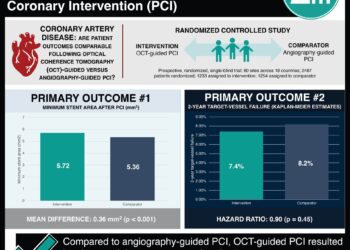
CTA as an alternative to angiography for blunt cerebrovascular trauma detection
Image: PD
1. Detection of blunt carotid/vertebral injury (BCVI) with computed tomography angiography (CTA) is reliable in patients with two of the following risk factors: cervical spine fracture, skull base fracture, Horner’s syndrome, neck soft tissue injury or unexplained neurological deficit.
2. CTA also has a high false-negative rate and a negative CTA for BCVI should prompt further investigation with digital subtraction angiography.
Study Rundown: CTA accuracy in detecting blunt cerebral and vertebral artery injury varies considerably across clinical settings. This study is rapid and noninvasive, but CTA has low sensitivity in detecting cerebrovascular injury compared to digital subtraction angiography. Therefore, a negative CTA should not rule out BCVI, but a positive CTA in a high-risk patient could be used as an indication to start treatment in order to avoid further complications such as stroke. This meta-analysis was limited by the quality and heterogeneity of the available studies. Some of the included studies did not specify severity of neck injury, others did not define a positive CTA result, and two studies did not specify if the radiologists were blinded to DSA results. Only three of the eight studies enrolled patients consecutively. There was a wide variety in the quality of CTA studies that were conducted with the number of slices ranging from 1 to 64. This investigation’s strength was its thorough statistical analysis that explored pooled accuracy measures for both any BCVI and single artery injury alone with and without outlier studies.
Click to read the study in Annals of Surgery
In Depth [systematic review and meta-analysis]: This study included 8 diagnostic accuracy studies that examined the reliability of computed tomography angiography in evaluating blunt cerebral and vertebral artery injury (BCVI) compared to digital subtraction angiography (DSA). More than half of the studies were prospective and all were conducted at level I trauma centers in the US between 2002 and 2011. There was significant heterogeneity in number of slices available on CT machines used and reading radiologist’s level of training. CTA’s ability to detect BCVI compared to DSA had estimated sensitivity of 66% and specificity of 97% with corresponding positive likelihood ratio of 20% and negative likelihood ratio of 0.35%. With further statistical analysis, studies read by neuroradiologists did not have significantly higher sensitivity, and CTs with higher slice numbers did not provide sensitivity higher than 75%.
By Asya Ofshteyn and Allen Ho
More from this author: Low infection risk with neurologic endovascular procedures, Post-operative PTSD intervention improves physical outcomes in trauma patients, Hep B reactivation common after liver resection for HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma, CABG leads to fewer MIs and repeat revascularization vs. stenting
© 2013 2minutemedicine.com. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without written consent from 2minutemedicine.com. Disclaimer: We present factual information directly from peer reviewed medical journals. No post should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2minutemedicine.com. PLEASE SEE A HEALTHCARE PROVIDER IN YOUR AREA IF YOU SEEK MEDICAL ADVICE OF ANY SORT. Content is produced in accordance with fair use copyrights solely and strictly for the purpose of teaching, news and criticism. No benefit, monetary or otherwise, is realized by any participants or the owner of this domain.