Dapagliflozin associated with reduced risk of total heart failure events and cardiovascular death
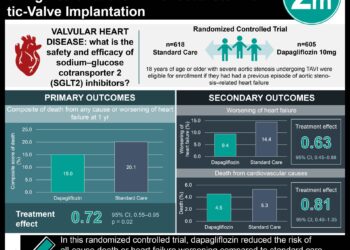
1. In this prespecified analysis of the DELIVER trial, among 6263 patients, dapagliflozin reduced the risk of total heart failure (HF) events and cardiovascular death by 23%.
2. There were 1057 HF events and cardiovascular deaths in the placebo group, compared with 815 in the dapagliflozin group.
Evidence Rating Level:1 (Excellent)
Study Rundown: Patients living with heart failure (HF) are frequently hospitalized for decompensation of HF, with the risk for hospitalization remaining consistent across the spectrum of ejection fraction (EF). Repeated hospitalizations contribute significantly to the burden of HF on patients and healthcare systems. This prespecified analysis of the Dapagliflozin Evaluation to Improve the Lives of Patients with Preserved Ejection Fraction Heart Failure (DELIVER) trial evaluated the effect of dapagliflozin on the total (first and recurrent) HF events and cardiovascular death in patients with HF. Patients with HF with mildly reduced EF or HF with preserved EF were randomized to receive either dapagliflozin 10 mg once daily or a placebo. The primary outcome of the DELIVER trial was total episodes of worsening HF and cardiovascular death. Among the 6263 patients included, there were 1057 HF events and cardiovascular deaths in the placebo group and 815 in the dapagliflozin group. Patients with more HF events were found to have features of more severe HF, such as higher N-terminal pro-B type natriuretic peptide levels, poor kidney function, prior HF hospitalizations, and longer duration of HF. In the Lin, Wei, Yang, and Ying model (LWYY), the rate ratio for total HF events and cardiovascular death for dapagliflozin vs placebo was 0.77. In the joint frailty model, the rate ratio was 0.72 for total HF events and 0.87 for cardiovascular death. Strengths of this study include its large sample size and rigorous analysis. However, a limitation was that follow-up was limited; therefore, the full lifetime burden of HF events of deaths in each treatment group was unknown. Overall, dapagliflozin demonstrated no reduction in efficacy in reducing second or subsequent HF events.
Click to read the study in JAMA Cardiology
Relevant Reading: Dapagliflozin in patients with heart failure and reduced ejection fraction
In-Depth [randomized controlled trial]: This study evaluated the effect of dapagliflozin on total HF events and cardiovascular death in patients with HF with mildly reduced or preserved EF. The main outcomes were total episodes of worsening HF (hospitalization for HF or urgent HF visit requiring intravenous HF therapies) and cardiovascular death. A total of 6263 patients were included, 2747 (43.9%) were women, and the mean (SD) age was 71.7 (9.6) years. Among 6263 patients, during a median (IQR) follow-up of 2.3 (1.7-2.8) years, a total of 1380 nonfatal worsening HF events occurred in 822 patients. Most patients had 1 or 2 worsening HF events during follow-up, with a maximum of 16 events. There were 212 fewer worsening HF events and 30 fewer total cardiovascular deaths in the dapagliflozin group compared with the placebo group. The rate of total HF events and cardiovascular death was 15.3 per 100 patient-years in the placebo group compared to 11.8 per 100 patient-years in the intervention group, with a reduction of 3.5 events per 100 patient-years of follow-up. In LWYY model, the rate ratio for total HF events and cardiovascular death for dapagliflozin vs placebo was 0.77 (95% CI, 0.67 – 0.89; P < .001) compared with a hazard ratio of 0.82 (95% CI, 0.73 – 0.92; P < .001) in a time to first even analysis. In the join frailty mode, the rate ratio was 0.72 (95% CI, 0.65 – 0.81; P < .001) for total HF events and 0.87 (95% CI, 0.72 – 1.05; P = .14) for cardiovascular death.
Image: PD
©2023 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.