Micronutrient supplementation linked with decreased HIV-disease progression
Image: PD
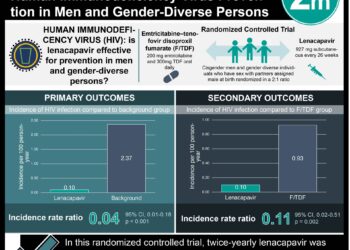
1. Supplementation with multivitamin plus selenium decreased risk of developing a CD4 cell count of 350/μL in ART-naïve HIV-infected patients.
2. Multivitamin plus selenium supplementation did not increase risk of HIV or health-related adverse events.
Evidence Rating Level: 2 (Good)
Study Rundown: Despite its known efficacy, access to antiretroviral therapy (ART) is limited in resource poor settings. Micronutrients such as B vitamins, vitamin C and E, and selenium are known to be a crucial component of a robust immune system. Previous research has shown that micronutrient supplementation increased CD4 count and decreased viral load in late stages of HIV infection. This study examined the effect of certain micronutrient supplements on immune function and disease progression in the early stages of HIV. The authors found that supplementation with a single daily pill of multivitamin plus selenium significantly reduced the risk of developing a CD4 count of 350/μL and a combined outcome of CD4 <350/μL, AIDS-defining conditions, or AIDS-related death compared to placebo. Micronutrient supplementation did not increase the risk of adverse events and was determined to be safe. This study was performed in a resource poor setting and in patients with HIV-subtype C, which is known to accelerate disease progression. Overall, these findings provide support for an effective alternative intervention to prevent early HIV disease progression in areas where ART is not readily available.
Click to read the study in JAMA
Relevant Reading: Micronutrients in HIV-positive persons receiving highly active antiretroviral therapy
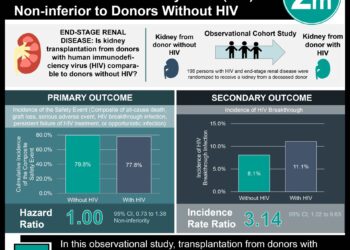
In-Depth [randomized controlled trial]: This double blind, placebo controlled clinical trial randomized 878 HIV subtype C-infected, ART-naïve Botswanan adults with CD4 cell count greater than 350/μL into four study groups. Each group received a single daily pill of multivitamin alone, selenium alone, multivitamin plus selenium, or placebo. Participants were assessed every 3 months for an average total duration of 24 months. Treatment with multivitamin plus selenium (p=0.02, HR 0.48, 95% CI: 0.26-0.88) and multivitamin alone (p=0.04, HR 0.54, 95% CI: 0.30-0.98) significantly reduced the risk of developing a CD4 count of 250/μL or less while selenium alone had no effect (p=0.50, HR 0.83, 95% CI: 0.48-1.42). Multivitamin plus selenium supplementation also significantly reduced the risk of obtaining the composite outcome of CD4 <350/μL, AIDS-defining conditions, or AIDS-related death (p = 0.045, HR 0.65, 95% CI: 0.43-0.99). HIV viral load was not significantly different between any of the study groups. Of 78 participants, 79 serious adverse advents were reported, none of which were deemed related to the intervention. No significant differences in HIV-related and health related adverse events were found between the four groups.
By Jonathan Lichkus and Rif Rahman
More from this author: Obesity without metabolic syndrome still associated with increased mortality, Childhood poverty may harm brain development, Prostate-Specific Antigen screening of elderly men varies significantly in primary care, Younger women more likely than men to present with acute coronary syndrome without chest pain
© 2012-2013 2minutemedicine.com. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2minutemedicine.com. Disclaimer: We present factual information directly from peer reviewed medical journals. No post should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors, editors, staff or by 2minutemedicine.com. PLEASE SEE A HEALTHCARE PROVIDER IN YOUR AREA IF YOU SEEK MEDICAL ADVICE OF ANY SORT.