Non-surgical outpatient treatment for CIN shows promise
1. Patients with CIN-2 who were treated with hexaminolevulinate 5% photodynamic therapy showed histological improvement.
2. This treatment method also demonstrated efficacy at clearance of HPV in patients with CIN-2.
Evidence Rating Level: 1 (Excellent)
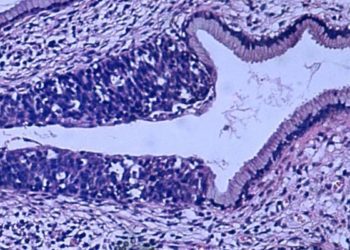
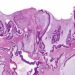
Study Rundown: Worldwide, cervical cancer is the leading causes of cancer death for women. Existing practices, such as the human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine and routine screening with Pap smears, reduce the incidence of and facilitate early identification of cervical malignancies. Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) is a precursor to malignancy identified on cytology. Among women over 24 years old, current guidelines recommend observation for low-grade (CIN-1), as many of these lesions regress on their own. Those with high-grade lesion (CIN-2 or 3) are recommended to undergo excision by conization or loop electrosurgical excision procedure. While effective in removing pre-malignant or localized malignant lesions, these procedures are not without morbidity and may increase risk for preterm birth. Previous work has shown that hexaminolevulinate (HAL) photodynamic therapy (PDT) is effective in treating CIN. The present study is the first to evaluate the efficacy, safety, dosing and side effects of an outpatient HAL PDT treatment. Authors found that HAL PDT was effective in managing CIN-2 with minor side effects.
Strengths of the study included a double-blinded, randomized controlled trial study design. Limitations included a relatively short follow-up period and patient removal of the device, which may have resulted in minor variations in treatment time with HAL PDT. Future work should include Phase 3 trials in a larger population. Longer-term follow up would assess for sustained response to treatment and identify long-term adverse effects.
Click to read the study in AJOG
In-Depth [randomized controlled trial]: This study evaluated the efficacy of HAL PDT in treatment of women with CIN-1 or CIN-2. Women were randomized to receive either placebo (n=68), HAL 0.2% (n=62), HAL 1% (n=67) or HAL 5% (n=65). Outcomes of interest were clinical response to treatment, defined as normal histology or low-grade cytology with clearance of oncogenic HPV infection present at baseline and adverse effects.
In patients with CIN-2, those receiving HAL 5% showed a 95% response rate (p=0.009) at 3 months and 6 months. This group also demonstrated better clearance of HPV, with 62% clearance at 3 months and 77% clearance at 6 months compared to 28% and 39% in the placebo group, respectively, though these differences were not statistically significant. A greater proportion of patients receiving HAL 5% reported experiencing adverse side effects, the most common of which were discharge, local discomfort and spotting.
More from this author: Obstetric scoring systems overestimate cases of severe sepsis, Vitamin D deficiency linked to preeclampsia, Cervical ripening with isosorbide mononitrate linked to increased side effects
Image: PD
©2014 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors, editors, staff or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.