Quick Take: Diagnosis of obstructive coronary artery disease using computed tomography angiography in patients with stable chest pain depending on clinical probability and in clinically important subgroups
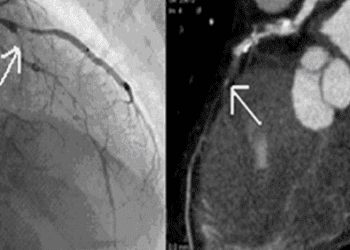
Computed tomography angiography (CTA) is being increasingly used in evaluating patients with suspected coronary artery disease (CAD) and possible angina. It is currently unclear, however, which patient subgroups in which CTA demonstrates the highest diagnostic clinical performance. In this meta-analysis, individual patient data (n=5332) from 64 prospective diagnostic accuracy studies was used to determine whether CTA should be performed in patients with any clinical probability of CAD, and whether the diagnostic performance of this test differs between patient subgroups. For a pretest probability range of 7% to 67%, the treat threshold of more than 50% and the no-treat threshold of less than 15% post-test probability were obtained using CTA. Researchers found that at a pretest probability of 7%, the positive predictive value of CTA was 50.9% (95% CI 43.3% to 57.7%) and the negative predictive value of CTA was 97.8% (95% CI 96.4% to 98.7%). The corresponding values at a pretest probability of 67% were 82.7% (95% CI 78.3% to 86.2%) and 85.0% (95% CI 80.2% to 88.9%), respectively. The sensitivity of CTA was 95.2% (95% CI 92.6% to 96.9%) while the specificity was 79.2% (95% CI 74.9% to 82.9%). The area under the receiver-operating-characteristic (ROC) curve for CTA was 0.897 (95% CI 0.889 to 0.906). Importantly, the diagnostic performance of CTA was slightly lower in patients older than 75, with an area under the ROC curve of 0.864 (95% CI 0.834 to 0.894) when compared to all other age groups (p=0.018). The diagnostic performance of CTA was also slightly lower in women (p<0.001). The diagnostic performance was not significantly influenced by angina pectoris type. This study therefore shows that the diagnosis of obstructive CAD using coronary CTA in patients with stable chest pain was most accurate when the clinical pretest probability was between 7% and 67%. The performance of CTA was not influenced by angina pectoris type and was slightly lower in older patients and in women.
Click to read the study in BMJ
©2019 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.