Quick Take: Pexidartinib versus placebo for advanced tenosynovial giant cell tumour (ENLIVEN)
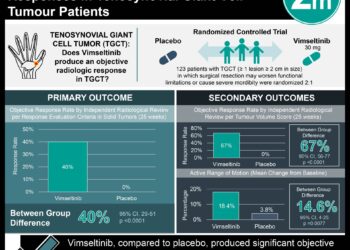
Tenosynovial giant cell tumor (TGCT) is a rare mesenchymal neoplasm that arises in the joints, bursae, or tendon sheaths. The standard treatment is surgical resection, but recurrence is common. Repeated surgery in these patients also carries a risk of increasing morbidity and mortality. Unfortunately, no systemic therapies currently exist. Pexidartinib is a novel small molecule tyrosine-kinase inhibitor which has shown clinical efficacy against recurrent or inoperable TGCT in a phase 1 study. In part one of this randomized controlled trial, 120 patients with advanced TGCT for whom surgery was not recommended were assigned to receive pexidartinib therapy or placebo to study the impact on overall disease response (complete or partial response) at week 25 based on MRI. In part two of the study, all patients received pexidartinib. Due to the emergence of mixed or cholestatic hepatotoxicity, the data monitoring committee stopped enrollment six patients short of the target study population of 126. Researchers found that more patients in the pexidartinib group achieved overall disease response at week 25 than in the placebo group (39% vs. 0%, difference 39%, 95% CI 27% to 53%, p<0.0001). At 6 months, no patient who responded to pexidartinib at week 25 had progressed. Serious adverse events occurred in 13% of patients in the pexidartinib group and in 2% of patients in the placebo group. These cases included three patients in the pexidartinib group who experienced mixed or cholestatic hepatotoxicity, two of which recovered, while the other case lasted 7 months and was confirmed by liver biopsy. Hair color changes (67%), fatigue (54%), and aspartate aminotransferase increase (39%) were the most frequent pexidartinib-associated adverse events. This study was limited by early termination of patient enrollment. Overall, this study suggests that pexidartinib therapy may have significant clinical efficacy in the treatment of advanced TGCT. However, the potential therapeutic benefits of pexidartinib should be weighed against the risk of mixed and cholestatic hepatotoxicity.
Click to read the study in Lancet
Image: PD
©2019 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.