Social media interventions may improve physical activity and mental wellness
1. In this meta-analysis, the impact of interactive social media interventions aimed at increasing physical activity was evaluated.
2. Improvements were seen in daily steps taken, marginal weight loss, reducing heart rate, and overall well-being.
Evidence Rating Level: 2 (Good)
Social media use has increased substantially since the introduction of programs such as Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter. Additionally, access to the internet has created a platform for the remote delivery of wellness and physical activity interventions. Social media may represent an interactive strategy for engaging users in physical and mental wellness activities.
The researchers analyzed the current literature on the effectiveness of interactive social media interventions focused on physical activity and mental wellbeing. Inclusion criteria were randomized control trials, controlled before-and-after studies, and interrupted time series which used an interactive online intervention to improve health behaviours in adults. Studies were excluded if the program that was evaluated had no social component. Study outcomes included physical health, mental health, adverse outcomes, and sub-group analysis to assess health equity.
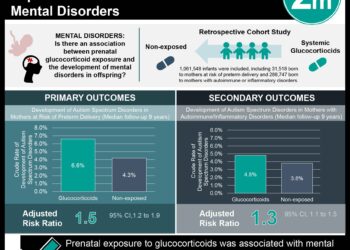
A total of 88 studies were included in the meta-analysis, with a total of 871,378 participants. Improvements were seen in daily steps, weight loss, resting heart rate, and overall well-being. No adverse effects were reported, and no changes were seen in diet composition, tobacco use, and depression. Limitations included heterogeneity of programs used, evaluation metrics, and study population. In summary, this study suggested social media interventions may improve overall health behaviour, but have limited impact on metrics such as smoking cessation.
Click to read the study in Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews
Image: PD
©2021 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.