Vasopessin not shown to improve kidney function or clinical outcomes in septic shock
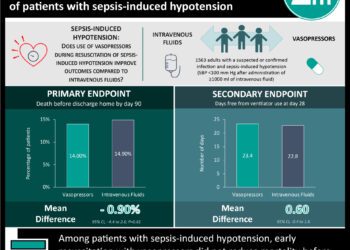
1. There was no significant difference in 28-day mortality between those receiving vasopressin vs. norepinephrine.
2. There was no significant difference in the number of days free from kidney failure between those who received vasopressin vs. norepinephrine.
Evidence Rating Level: 1 (Excellent)
Study Rundown: Septic shock is estimated to cause 400 000 deaths per year in the United States. Intravenous fluids and vasopressor support (primarily with norepinephrine) is used to maintain adequate perfusion to vital organs and is the mainstay of treatment. Recent studies have shown that another vasopressor, vasopressin, may help maintain organ function better than norepinephrine. The VANISH trial found that there was no significant difference in 28-day mortality nor number of days free from kidney failure between those who received vasopressin and those who received norepinephrine.
While this randomized controlled trial was designed to differentiate the outcomes of patients with septic shock who received vasopressin or norepinephrine, the cohort in the trial was relatively non-sick. Thus, few patients developed kidney failure while in the study, limiting the power of the study to find a difference in outcomes. The results of this study should be considered in the context of its relatively healthy cohort, however, larger studies are warranted to assess what role vasopressin may play in severely ill patients.
Click to read the study, published today in JAMA
Relevant Reading: Vasopressin or norepinephrine in early hyperdynamic septic shock: a randomized, clinical trial
In-Depth [randomized controlled trial]: The VANISH trial was a randomized, double-blinded multicenter study conducted at 18 ICUs in the United Kingdom. It randomized patients with septic shock to vasopressin + placebo, norepinephrine + placebo, vasopressin + hydrocortisone, and norepinephrine + hydrocortisone in a 2×2 factorial design. Patients who had end-stage renal disease, contraindication to vasopressors, another requirement for steroid administration, and those who had already received vasopressor therapy during the ICU admission were excluded. Hydrocortisone or placebo was only added once maximum titration doses of vasopressin (0.06 U/min) and norepinephrine (12 mcg/min) were reached. The initial primary outcome was the number of days free from kidney failure, but given that the majority of patients did not develop kidney failure, the cohort was split into two groups (those who developed kidney failure and those who did not) and the primary outcome was applied to the cohort that developed kidney failure and/or died.
Results demonstrated that 57.0% of the vasopressin group and 59.2% of the norepinephrine group did not develop renal failure (p = 0.88). In the patients who died, the median number of days prior to kidney-failure in the vasopressin group compared to the norepinephrine group was 9 vs. 13 (with absolute difference of -4 days, 95%CI -11 to 5). There was no significant difference in 28-day mortality rates between the two groups (30.9% for vasopressin vs. 27.5% for norepinephrine, absolute difference 3.4%, 95%CI -5.4% to 12.3%), nor was there any significant difference in mortality rates between those who received hydrocortisone vs. placebo.
Image: CC/Wiki
©2016 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.