
Want more physician-written
medical news?
Join over 10 million yearly readers and numerous companies. For healthcare professionals
and the public.
Subscribe for free today!
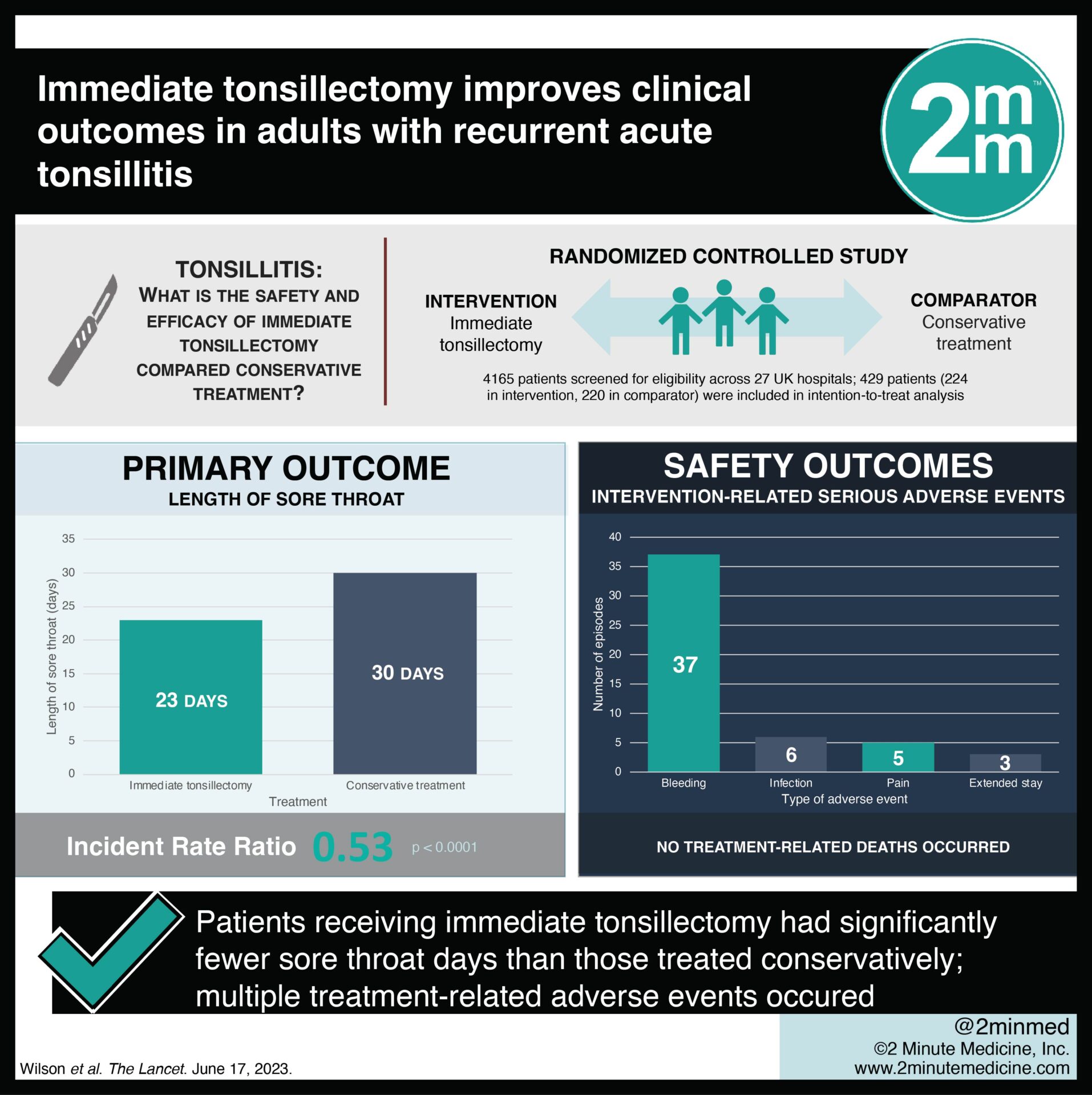 1. Patients assigned to immediate tonsillectomy had significantly fewer sore throat days than those receiving conservative management.
1. Patients assigned to immediate tonsillectomy had significantly fewer sore throat days than those receiving conservative management.
2. Bleeding near the surgical site was the most common adverse event in the tonsillectomy group.
Evidence Rating Level: 1 (Excellent)
Study Rundown: Adults with recurrent tonsilitis often undergo tonsillectomy. A reduction in tonsillectomies has been associated with increased recurrent acute tonsillitis; however, the extent to which immediate tonsillectomy improves clinical outcomes in patients with recurrent acute tonsillitis is unknown. This randomized controlled trial aimed to assess the safety and efficacy of immediate tonsillectomy versus conservative treatment in patients with recurrent acute tonsilitis. The primary outcome of this study was the number of sore throat days for the first 24 months while the key secondary outcome included a Tonsillectomy Outcome Inventory-14 (TOI-14) score at regular study intervals. According to study results, patients with immediate tonsillectomy reported significantly fewer sore throat days compared to those with conservative management. This study was strengthened by a randomized design with a large sample size and longitudinal design, thus increasing its validity.
In-depth [randomized controlled trial]: Between May 11, 2015, and Apr 30, 2018, 4165 patients were screened for eligibility across 27 hospitals in the United Kingdom (UK). Included were patients ≥ 16 years with recurrent acute tonsilitis. Altogether, 429 patients (224 in immediate tonsillectomy and 220 in conservative management) were included in the intention-to-treat analysis. The median age of patients was 23 years (interquartile range [IQR] 19-30) and the majority were white (90%) females (78%). The primary outcome of sore throat was reduced (incident rate ratio [IRR] 0.53, p<0.0001) in the immediate tonsillectomy group (23 days, IQR 11-46) compared to conservative treatment (30 days, IQR 14-65). The most common adverse event was bleeding (19%) and there were no treatment-related deaths. Findings from this study suggest that immediate tonsillectomy is safe and cost-effective in patients with recurrent acute tonsilitis.
©2023 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.
2 Minute Medicine is the leading authoritative medical news licensing service, and the only with reports written by practicing doctors.

No ads & unlimited access to all current reports, over 9000 searchable archived reports, visual abstracts, Weekly Rewinds, and the online edition of The Classics Series™ textbook.
2 Minute Medicine® is an award winning, physician-run, expert medical media company. Our content is curated, written and edited by practicing health professionals who have clinical and scientific expertise in their field of reporting. Our editorial management team is comprised of highly-trained MD physicians. Join numerous brands, companies, and hospitals who trust our licensed content.
© 2021 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. - Physician-written medical news.
© 2021 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. - Physician-written medical news.

Join over 10 million yearly readers and numerous companies. For healthcare professionals
and the public.
Subscribe for free today!