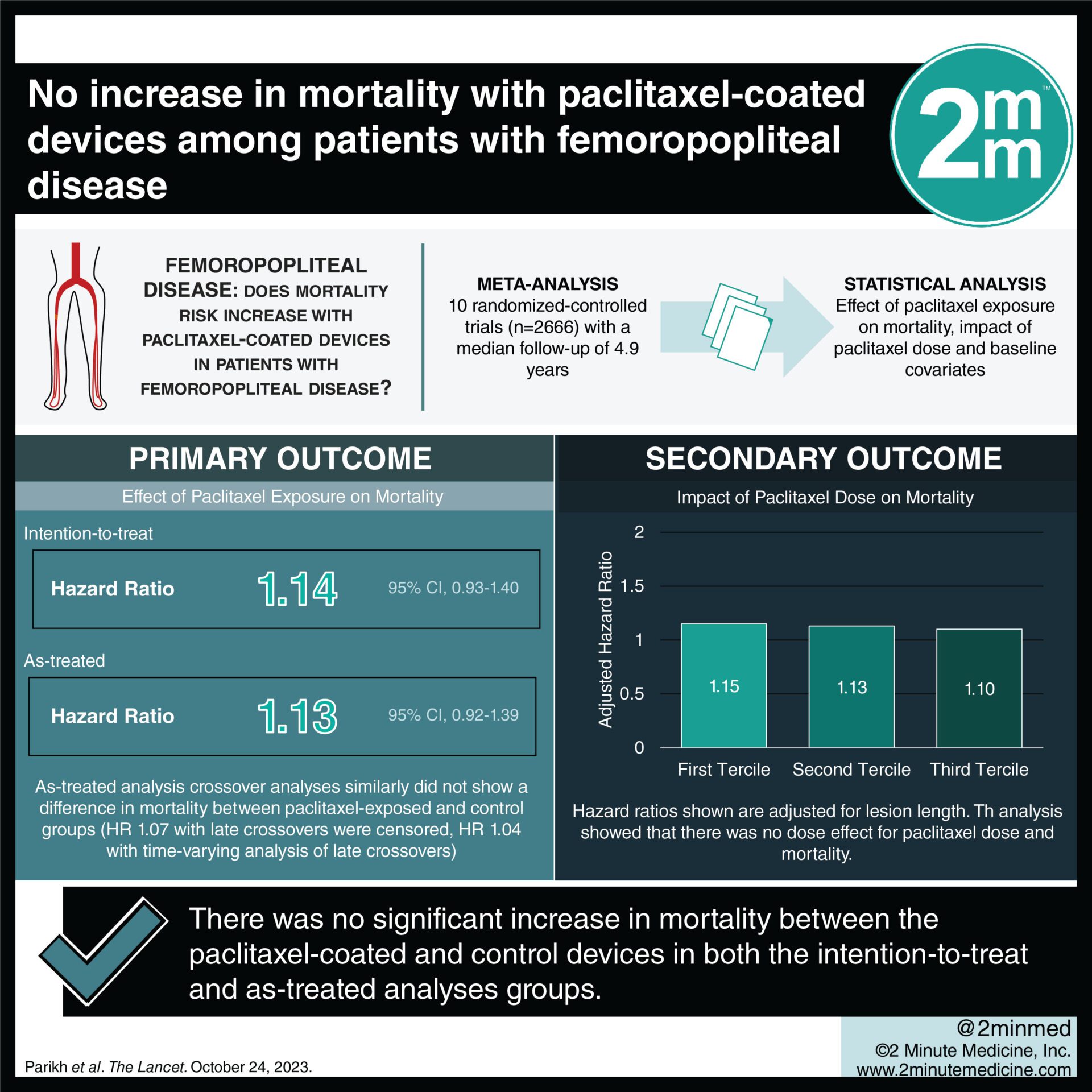
#VisualAbstract: No increase in mortality with paclitaxel-coated devices among patients with femoropopliteal disease
1. There was no significant increase in mortality between the paclitaxel-coated and control devices in both the intention-to-treat and as-treated analyses groups.
Evidence Rating Level: 1 (Excellent)
Study Rundown: The safety of paclitaxel-coated devices for femoropopliteal disease has been well-studied; however, a 2018 meta-analysis raised concerns about increased mortality risk with paclitaxel. This meta-analysis aimed to provide updated insights on data from ten different trials comparing mortality rates between paclitaxel-coated and control (non-paclitaxel-coated) devices. The primary outcome was the effect of paclitaxel exposure on mortality, while key secondary outcomes were the impact of paclitaxel dose and baseline covariates. According to study results, there was no significant increase in mortality between the paclitaxel-coated and non-paclitaxel-coated devices. Although this study was well done, it was limited by variability in trial design and patient populations, affecting the validity of results.
Click to read the study in The Lancet
Relevant Reading: Mortality with Paclitaxel-Coated Devices in Peripheral Artery Disease
In-depth [meta-analysis]: Between 2005 and 2018, 10 trials were included comparing paclitaxel-coated versus control devices for femoropopliteal occlusive disease. Altogether, 2666 patients were included in the final analysis, with a median follow-up of 4.9 years. The primary outcome reported no significant increase in deaths associated with paclitaxel-coated devices (hazard ratio [HR] 1.14, 95% confidence interval [CI] 0.93-1.40). Similarly, the unadjusted HR for all-cause mortality comparing paclitaxel-coated and control-treated participants was 1.02 (95% CI 0.78-1.34), offering reassurance to patients, physicians, and regulators on their safety. Overall, findings from this study suggest that paclitaxel-coated devices do not pose an increased risk of mortality.
©2023 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.



![siRNA against antithrombin alleviates symptoms of hemophilia [PreClinical]](https://www.2minutemedicine.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/04/clot-CCWiki-350x250.jpg)


